
Subsequent unions of states included the first and second Swiss Confederations (1291–17–48), the United Provinces of the Netherlands (1579–1795), the German Bund (1815–66), the first American union known as the Confederation of the United States of America (1781–89), and second American union formed as the United States of America (1789–1865).

Unlike the Greek city states of Classical Greece, each of which insisted on keeping its complete independence, changing conditions in the Hellenistic period drove many city states to band together even at the cost of losing part of their sovereignty. An early progenitor of federalism was the Achaean League in Hellenistic Greece. were the Archaic League, the Aetolic League, the Peloponnesian League, and the Delian League. Some examples from the seventh to second century B.C. The first forms of federalism took place in ancient times, in the form of alliances between states. Political scientists, however, use it in a much broader sense, referring instead to a "multi-layer or pluralistic concept of social and political life." In the narrow sense, federalism refers to the mode in which the body politic of a state is organized internally, and this is the meaning most often used in modern times. Some characterize the European Union as the pioneering example of federalism in a multi-state setting, in a concept termed the "federal union of states". Įxamples of a federation or federal province or state include Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Brazil, Iraq, Canada, Germany, UAE, Mexico, India, Malaysia, Nepal, Nigeria, Pakistan, Russia, Switzerland, and United States. It represents the central form in the pathway of regional integration or separation, bounded on the less integrated side by confederalism and on the more integrated side by devolution within a unitary state. įederalism differs from confederalism, in which the general level of government is subordinate to the regional level, and from devolution within a unitary state, in which the regional level of government is subordinate to the general level. Federalism in the modern era was first adopted in the unions of states during the Old Swiss Confederacy.
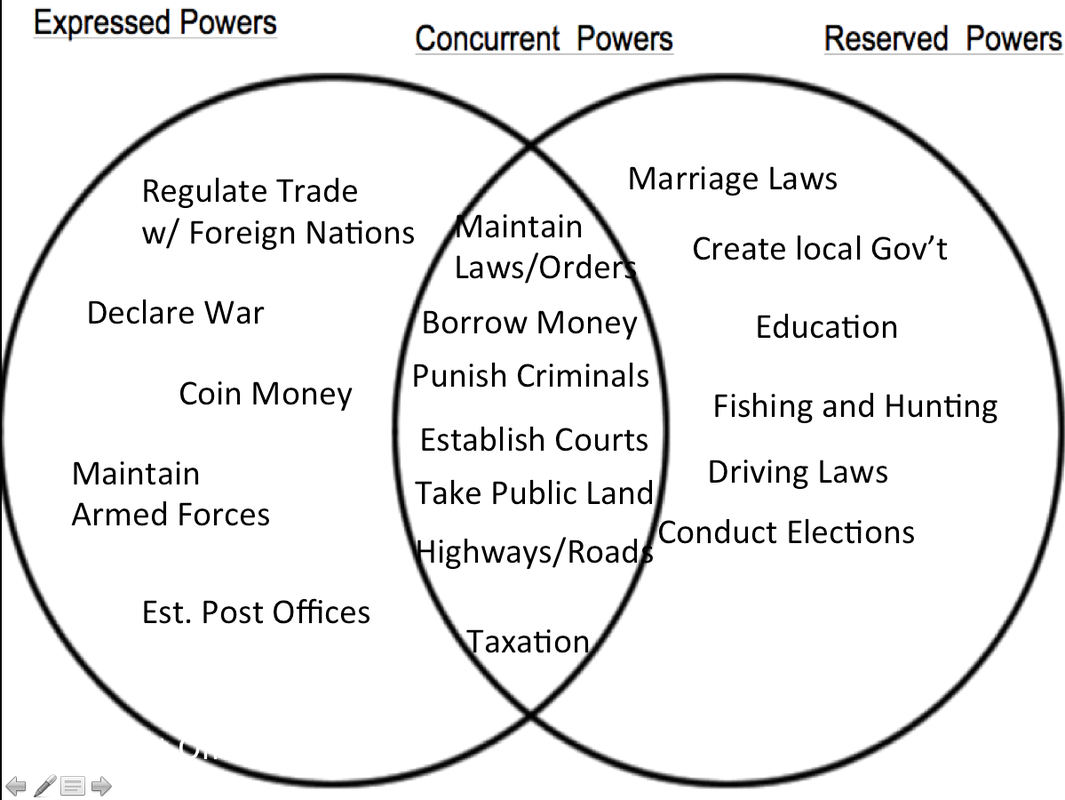
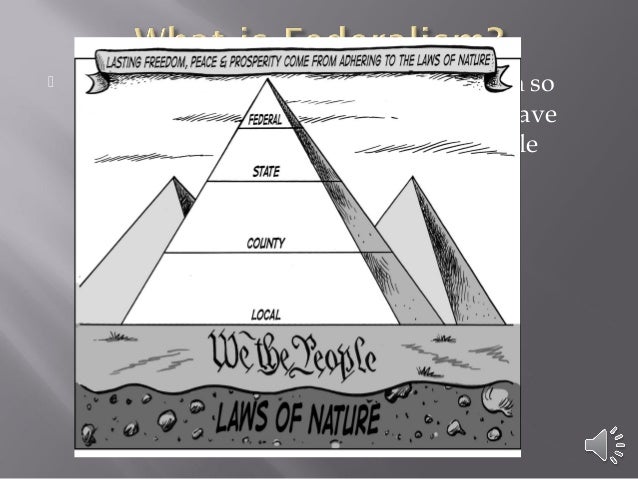
Federalism is a mixed or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments ( provincial, state, cantonal, territorial, or other sub-unit governments) in a single political system, dividing the powers between the two.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
